Prerequisite Before Building Mesos
Proxy
$ vim /etc/profile.d/proxy.sh
{
export http_proxy="http://web-proxy.houston.hp.com:8080/"
export https_proxy="https://web-proxy.houston.hp.com:8080/"
export ftp_proxy="http://web-proxy.houston.hp.com:8080/"
export no_proxy=localhost,10.0.0.0/8,16.0.0.0/8,127.0.0.1,192.168.20.0/24
use_proxy=on
}
Wget Proxy
$ vim /etc/wgetrc
https_proxy = http://web-proxy.houston.hp.com:8080/
http_proxy = http://web-proxy.houston.hp.com:8080/
use_proxy = on
Or build new file .wgetrc
# You can set the default proxies for Wget to use for http, https, and ftp.
# They will override the value in the environment.
https_proxy = http://127.0.0.1:8087/
http_proxy = http://127.0.0.1:8087/
ftp_proxy = http://127.0.0.1:8087/
# If you do not want to use proxy at all, set this to off.
use_proxy = on
use_proxy = on open the proxy, we can also use –Y in the command line:
-Y, --proxy=on/off open or close
Docker Proxy
$ vim /etc/sysconfig/docker
HTTP_PROXY="http://web-proxy.corp.xxxxxx.com:8080"
HTTPS_PROXY="http://web-proxy.corp.xxxxxx.com:8080"
http_proxy="${HTTP_PROXY}"
https_proxy="${HTTPS_PROXY}"
$ systemctl restart docker
Maven Proxy
Set proxy for mave or git
$ echo ${HOME}
$ cat ${HOME}/.m2/settings.xml
<settings>
<proxies>
<proxy>
<active>true</active>
<protocol>http</protocol>
<host>web-proxy.xxxxxx.com</host>
<port>8080</port>
</proxy>
</proxies>
</settings>
Git Proxy
Install socat .e.g. on SUSE
New-build this file gitproxy:
$ sudo vi /usr/bin/gitproxy
#!/bin/bash
PROXY=xxx.xxxx.com
PROXYPORT=8080
PROXYAUTH=username:password # If you have one.
exec socat STDIO PROXY:$PROXY:$1:$2,proxyport=$PROXYPORT,proxyauth=$PROXYAUTH
Then,
$ sudo chmod +x /usr/bin/gitproxy
$ chmod +x gitproxy
$ git config --global core.gitproxy gitproxy
Or execute the command in cmd-line:
git config --global http.proxy http://xxx-xxx.com:8080/
git config --global https.proxy https://xxx-xxx.com:8080/
Add docker.repo for yum
$ vim /etc/yum.repos.d/docker.repo
[dockerrepo]
name=Docker Repository
baseurl=https://yum.dockerproject.org/repo/main/centos/7/
proxy=https://web-proxy.houston.hp.com:8080/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://yum.dockerproject.org/gpg
Selinux
Selinux disabled or permissive.
Or
$ vim /etc/selinux/config
SELINUX=disabled
SSH
$mkdir ~/.ssh
$cd ~/.ssh
$ssh-keygen
$cat id_rsa.pub > authorized_keys
Then copy authorized_keys to other nodes of the cluster.
Env Of Mesos
# ls /usr/local/etc/mesos
Mesos-deploy-env.sh.template, mesos-master-env.sh.template, mesos-slave-env.sh.template.
We need to build the masters and slaves file, and copy mesos-deploy-env.sh, mesos-master-env.sh, mesos-slave-env.sh
1.In masters and slaves, if they non-existent, Build.
Masters: the name or IP of master
Slaves: the name or IP of slaves.
2.mesos-master-env.sh
About the configuration of master env.
export MESOS_log_dir=/var/log/mesos “log into”
export MESOS_work_dir=/var/lib/mesos “metadata into”
3.mesos-slave-env.sh
About the configuration of slave env.
export MESOS_master=IP:5050
export MESOS_log_dir=/var/log/mesos “log into”
export MESOS_work_dir=/var/run/mesos “for frameworks, default /tmp/mesos”
export MESOS_containerizers=docker,mesos
4.mesos-deploy.sh
Change nothing. Copy from the template.
Start the cluster
/usr/local/sbin there are some scripts. The mean as the name of the files.
Mesos-start-cluster.sh “start all of the cluster”
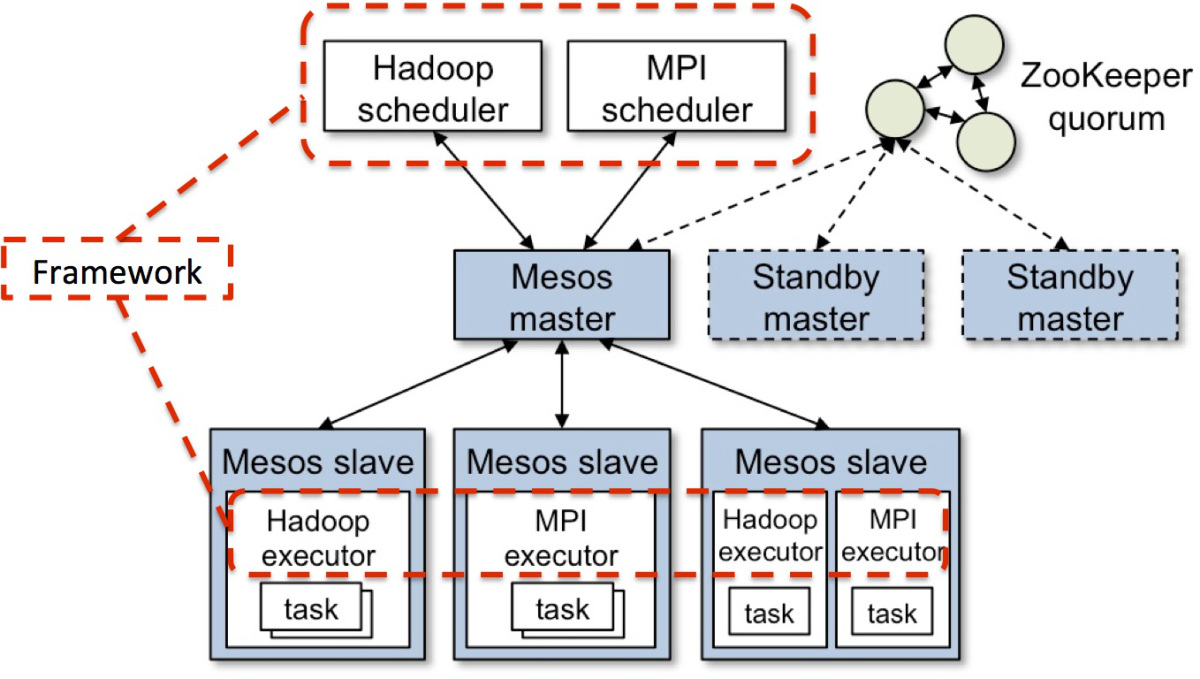
HA
In mesos-master-env.sh
export MESOS_log_dir=/var/log/mesos “log into”
export MESOS_work_dir=/var/lib/mesos “metadata into”
export MESOS_zk=zk://IP_1:2181,IP_2:2181,IP_3:2181/mesos
export MESOS_quorum=2
In mesos-agent-env.sh or mesos-slave-env.sh
export MESOS_master=zk://master_ip:2181/mesos
Marathon
Add
Export MESOS_NATIVE_JAVA_LIBRARY=/usr/local/mesos/lib/libmesos.so
Export MESOS_NATIVE_LIBRARY=/usr/local/mesos/lib/libmesos.so
Into /usr/local/marathon/bin/start (line2~line5)
Execute:
./bin/start –master zk://master_IP:2181/mesos –zk zk://master_ip:2181/marathon
Int the browser: master_ip:8080
Or
bin/start –master master_ip:5050 –zk zk://master_ip:2181/marathon
Zookeeper
$cd zookeepr/conf
$cp zoo_sample.cfg > zoo.cfg
#server.1=server_IP:2333:3222
#server.2=server_IP:2333:3222
$cd zookeepr && mkdir data && echo 1 > ./data/myid
Start zookpeer
./zookeeper/bin/zkServer.sh start
Slave on docker
Test:
$vim nginx.json
{
"id":"nginx",
"cpus":0.1,
"mem":10,
"instances": 1,
"constraints":[["hostname", "UNIQUE",""]],
"container": {
"type":"DOCKER",
"docker": {
"image": "nginx",
"network": "BRIDGE",
"portMappings": [
{"containerPort": 80,"hostPort": 0,"servicePort": 0, "protocol":"tcp" }
]
}
}
}